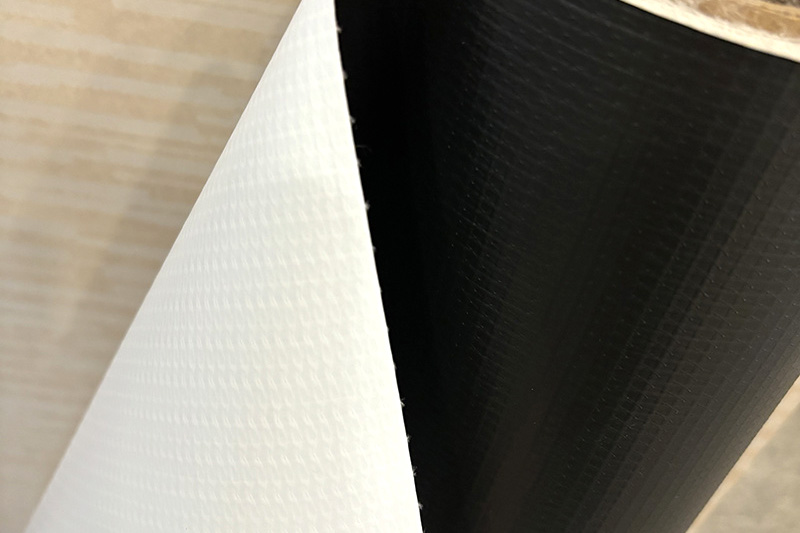
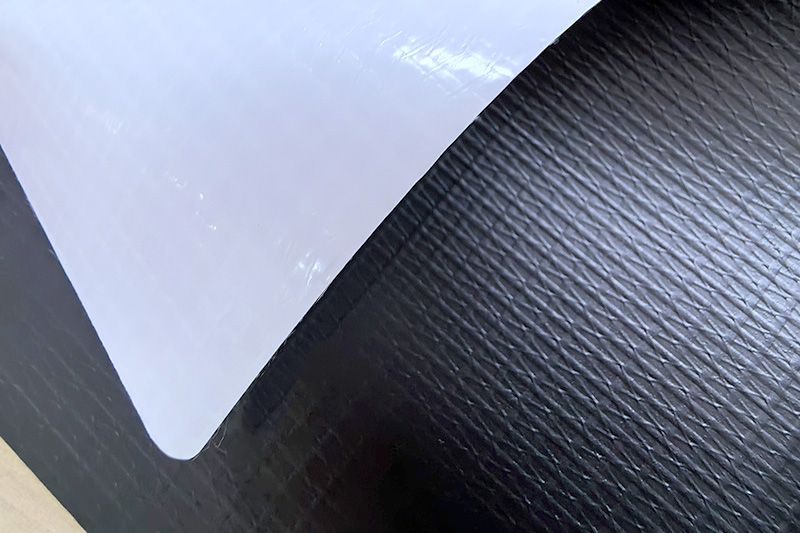
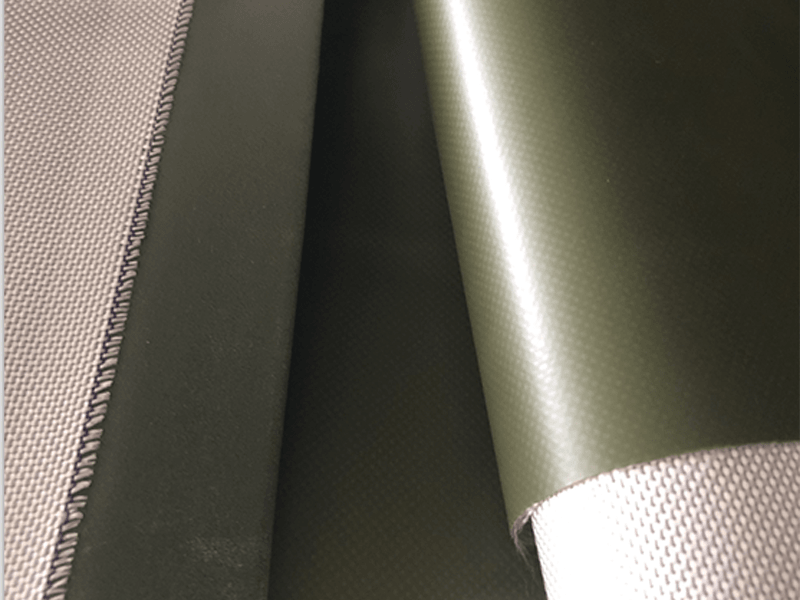
The balance between waterproofness and breathability in TPU fabric is achieved through several key factors. These factors help determine how well the fabric can repel water while allowing moisture vapor to escape, making it suitable for applications where both protection and comfort are required. The main factors include:
Thicker TPU Coating: A thicker TPU layer increases waterproofness by providing a more robust barrier against water. However, it can also reduce breathability, as a thicker layer makes it harder for moisture vapor (like sweat) to pass through.
A thinner TPU coating allows for better breathability since it makes it easier for moisture to escape. However, the waterproofing effect may be slightly reduced, as a thinner layer is less impervious to water.
TPU fabric can have a microporous membrane that features tiny pores. These pores are small enough to block liquid water but large enough to allow water vapor to pass through. The size, density, and distribution of these pores are crucial to balancing breathability and waterproofness.
Smaller and fewer pores result in better waterproofing but can hinder breathability.Larger or more pores improve breathability but might slightly compromise waterproofing.
TPU is often applied as a coating or laminate on a base fabric like polyester or nylon. The type of base fabric can affect both breathability and waterproofness. A more breathable base fabric will allow for better airflow and moisture management, while a more tightly woven fabric will enhance waterproofness.
In multi-layer TPU fabrics, the number of layers and the nature of each layer affect the overall balance. A layered fabric with TPU on one side and a breathable fabric on the other can provide good waterproofing and breathability.
TPU fabrics are engineered to have selective permeability, meaning they allow water vapor to escape while keeping liquid water out. The degree of this permeability depends on how the TPU is manufactured and processed. Fabrics with high water vapor permeability offer better breathability.
TPU is hydrophobic by nature, meaning it repels water, which enhances waterproofing. Its molecular structure can be engineered to allow moisture vapor to pass through without letting liquid water penetrate.
TPU is naturally flexible and elastic, which allows the fabric to maintain its integrity under tension. Flexibility can also enhance breathability by allowing micro-movements that facilitate airflow and moisture vapor release, without compromising waterproofness.
The performance of TPU fabric in balancing waterproofness and breathability can depend on external factors like temperature and humidity. In hot, humid environments, breathability is more critical, so fabrics are designed with thinner TPU layers or more micropores.
Intended Use: The specific application of TPU fabric determines how manufacturers prioritize waterproofness versus breathability. For instance, outdoor gear may focus more on waterproofness, while athletic wear may require more breathability.
Surface Treatments: Some TPU fabrics are treated with additional finishes or coatings to enhance specific properties. For example, a DWR (Durable Water Repellent) finish can be applied to increase water repellency without significantly affecting breathability.
Design Integration: In certain applications, TPU fabric is combined with ventilation features like mesh panels or vented seams to enhance breathability without compromising the waterproofing function of the main fabric.
The balance between waterproofness and breathability in TPU fabric is determined by the thickness of the TPU layer, the presence of a microporous structure, the characteristics of the base fabric, and the water vapor permeability of the TPU membrane. Flexibility, fabric layering, and environmental conditions also play a role in fine-tuning this balance for specific applications. By adjusting these factors, manufacturers can create TPU fabrics that meet the demands of different environments and uses.

 English
English русский
русский Français
Français Español
Español