In cold weather, PVC tarpaulin may become brittle or even crack due to low temperatures. This phenomenon is mainly due to the limited activity of the molecular chain of PVC materials under low temperature conditions, which reduces its elasticity and increases its fragility. To avoid this, the following measures can be taken:
Material improvement: Choose PVC tarpaulin with better cold resistance
Add plasticizers: Plasticizers (such as phthalates or environmentally friendly plasticizers) are usually added to PVC materials to improve flexibility and impact resistance. In cold environments, choosing PVC tarpaulin with a higher proportion of plasticizers can effectively reduce the risk of embrittlement.
Use modified PVC materials: Some manufacturers enhance the cold resistance of PVC through chemical modifications (such as the introduction of copolymers or elastomers). These modified materials can maintain good flexibility at low temperatures.
Pay attention to product specifications: When purchasing, you should choose PVC tarpaulin that is clearly marked as "cold-resistant" or "low-temperature suitable". Such products are usually specially formulated for cold environments.
Pretreatment before use
Temperature adaptation: Before using the PVC tarpaulin in cold weather, it should be placed indoors or in other warm environments for a period of time to gradually adapt to the ambient temperature. This can avoid changes in material stress caused by excessive temperature differences.
Avoid sudden cold and hot: If the PVC tarpaulin is directly exposed to the cold outdoor environment from a warm indoor environment, it may become brittle due to rapid cooling. Therefore, try to avoid drastic temperature fluctuations during use.
Proper installation and use
Reduce stretching and bending: In a low temperature environment, the flexibility of the PVC tarpaulin is reduced, and excessive stretching or bending may cause the material to crack. Therefore, excessive tension or sharp angle folding should be avoided during installation or use.
Avoid contact with sharp objects: PVC materials at low temperatures are more easily scratched or punctured, so special attention should be paid to avoid contact with sharp objects during use.
Appropriately loose installation: When fixing the PVC tarpaulin, do not pull it too tight, but leave a certain amount of slack so that the material has a buffer space when it shrinks at low temperatures.
Environmental protection measures
Insulation layer: If the PVC tarpaulin needs to be exposed to extreme cold for a long time, a layer of insulation material (such as foam board or felt) can be covered on its surface to slow down the impact of temperature on the material.
Avoid direct contact with ice and snow: PVC tarpaulin directly in contact with ice and snow may increase brittleness due to freezing. It is recommended to lay an isolation layer (such as wooden boards or plastic film) underneath it to reduce direct contact.
Regular inspection and maintenance
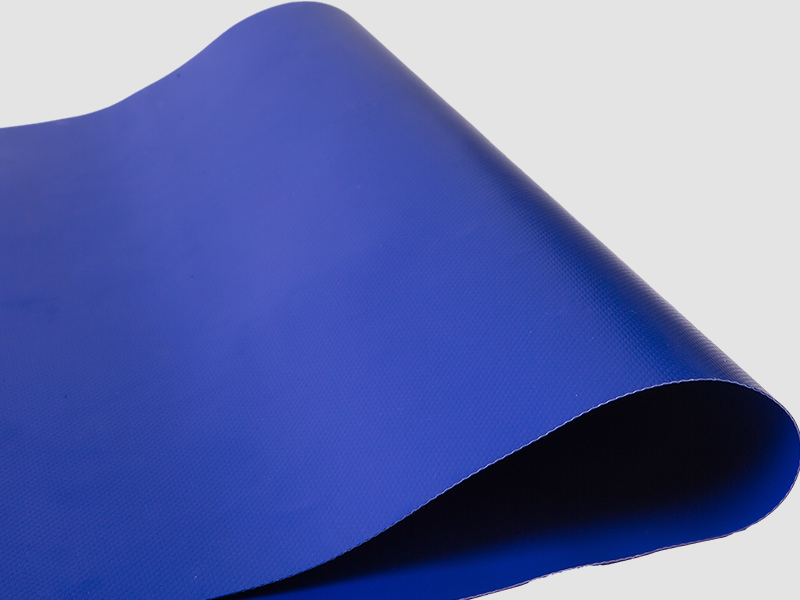
Regular inspection: In cold seasons, the PVC tarpaulin should be checked regularly for cracks or damage. Once a problem is found, it should be repaired or replaced in time.
Cleaning and maintenance: Keep the surface of the PVC tarpaulin clean to avoid the attachment of oil, chemicals or other contaminants, which may accelerate the aging of the material or reduce its cold resistance.
Storage precautions: When not in use, store the PVC tarpaulin in a dry and warm place to avoid long-term exposure to low temperature or humidity.
Alternatives: Choose other cold-resistant materials
If you are still concerned about the cold-resistant performance of PVC tarpaulins, you can consider using other alternative materials that are more suitable for cold environments, such as:
TPU tarpaulins: Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) has excellent cold resistance and flexibility, and can maintain good performance even in extremely low temperatures.
Silicone coated cloth: Silicone coated materials have excellent low-temperature resistance and are suitable for applications in extreme cold conditions.
Rubber composites: Certain rubber and PVC composite materials also have higher cold resistance.
In cold weather, the key to avoiding PVC tarpaulins from becoming brittle or cracking is to choose the right material, use it correctly and maintain it. By choosing PVC tarpaulins with better cold resistance, proper pretreatment, reasonable installation and strengthening daily maintenance, its service life can be significantly extended and its reliability in low-temperature environments can be ensured. If conditions permit, you can also consider using other alternative materials that are more suitable for cold environments to further improve safety and durability.

 English
English русский
русский Français
Français Español
Español